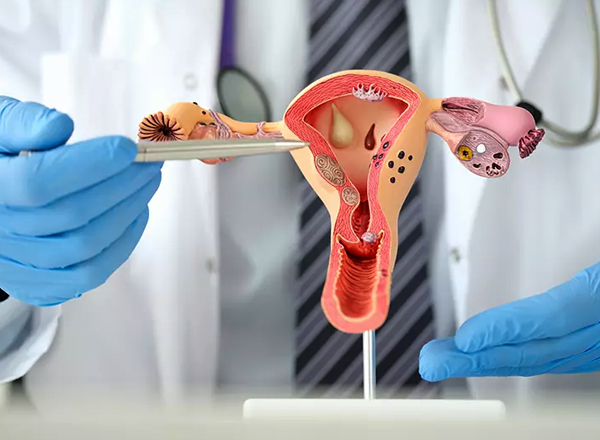
PCOS stands for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, which is a common hormonal disorder that affects people with ovaries, typically during their reproductive years. PCOS is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including:
-
Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Women with PCOS often experience irregular or infrequent menstrual periods.
-
Ovulatory Dysfunction: The ovaries may not regularly release eggs, leading to fertility issues.
-
Hyperandrogenism: Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) may cause physical symptoms such as acne, excessive facial or body hair (hirsutism), and male-pattern baldness.
-
Polycystic Ovaries: The ovaries may become enlarged and contain small follicles that surround the eggs, forming cysts.
-
Insulin Resistance: Some individuals with PCOS may have insulin resistance, which can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The exact cause of PCOS is not known, but both genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role. It is a common condition, and the symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
Management and treatment of PCOS typically involve addressing specific symptoms and may include lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications, regular exercise, and weight management. Medications may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, manage symptoms like acne and hirsutism, and improve insulin sensitivity. In some cases, fertility treatments may be recommended for those trying to conceive.
If you suspect you have PCOS or are experiencing symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
