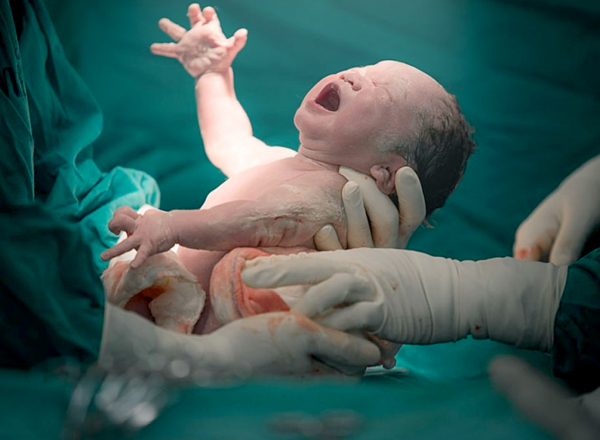
Normal vaginal delivery (NVD), also known as vaginal birth or natural birth, is the process of delivering a baby through the vagina. It is considered a natural and physiological way of giving birth when certain conditions allow for it. Here are key aspects of normal vaginal deliveries:
-
Labor Onset:
-
Labor typically begins when the body releases hormones that trigger contractions of the uterus.
-
The cervix dilates and effaces (thins out) to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal.
-
-
Stages of Labor:
-
First Stage: Early labor involves contractions that gradually become more regular and intense, leading to the opening of the cervix.
-
Active Phase: The cervix continues to dilate more rapidly.
-
Transition Phase: The final phase of the first stage, characterized by intense contractions and full cervical dilation.
-
Second Stage: The pushing stage, during which the baby is delivered through the birth canal. The mother actively pushes during contractions.
-
Third Stage: The delivery of the placenta, which usually occurs shortly after the baby is born.
-
-
Pain Management:
-
Pain relief options may include natural coping techniques, such as breathing exercises and movement.
-
Medical interventions, such as epidurals or other forms of pain medication, can be used based on the mother's preferences and medical condition.
-
-
Positioning:
-
Women often choose various positions during labor, such as walking, squatting, or using a birthing ball, to help facilitate the descent of the baby.
-
-
Monitoring:
-
Continuous monitoring of the baby's heart rate and the mother's vital signs is common during labor.
-
Intermittent vaginal exams are performed to assess cervical dilation and the baby's position.
-
-
Support:
-
Support from a birthing partner, family, or a doula can be beneficial during labor.
-
Midwives, obstetricians, and nurses provide medical support and guidance.
-
-
Flexibility:
-
Birth plans may outline preferences, but flexibility is important as labor can be unpredictable.
-
Healthcare providers make decisions based on the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
-
-
Immediate Postpartum Care:
-
Skin-to-skin contact between the mother and baby is encouraged shortly after delivery.
-
Breastfeeding may be initiated during the first hour after birth.
-
-
Recovery:
-
The recovery period after a normal vaginal delivery is generally shorter than after a cesarean section.
-
Postpartum care includes monitoring for any complications, managing pain, and providing support for breastfeeding and emotional well-being.
-
While many pregnancies are suitable for a normal vaginal delivery, it is important to note that individual circumstances may vary. Some factors, such as maternal health, fetal position, and potential complications, can influence the mode of delivery. Healthcare providers work closely with pregnant individuals to determine the most appropriate and safe approach for childbirth based on individual circumstances and preferences.
